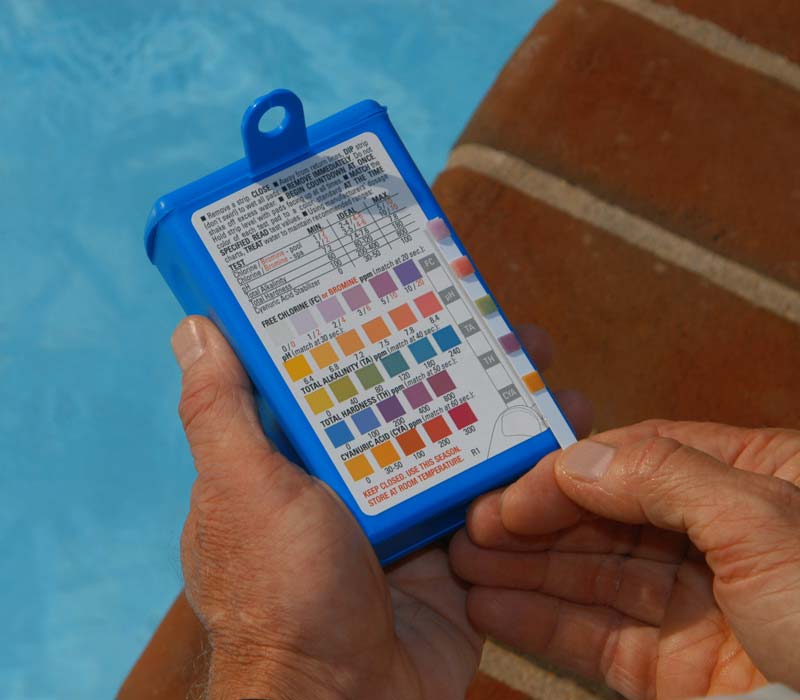
An intermediate look at pool and hot tub water chemistry and testing
Other available methods for sanitizing and oxidizing

1. Electrolytic salt chlorine generators (ECGs)
- ECGs pass an electric current through water containing 2500 to 5000+ ppm of sodium chloride (NaCl), forming chlorine gas (Cl2) at one electrode and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) at the other electrode.
- Cl2 reacts with water (H2O) to produce hypochlorous acid (HOCl).
- More than 3700 ppm sodium chloride will give water a slightly salty taste.
2. Ozonators
- Ozonators use either corona discharge or ultraviolet (UV) light to generate ozone (O3). In each process, air runs through a chamber, and oxygen is converted to O3, an unstable molecule.
- O3 is an oxidizer, not a sanitizer. A supplemental sanitizer must be used—generally chlorine or bromine.
- O3 has a half-life of about 18 minutes, so residuals cannot be maintained for normal disinfection.
3. Ionizers
- Ionizers generate copper and silver ions to provide algaecidal and extremely limited biocidal properties. Biocidal effectiveness is solely related to solubility of metal ions.
- An ionizer is not an oxidizer/sanitizer system; it requires a supplemental level of chlorine.
- Do not use bromine with ionizers as silver bromide may form. Silver bromide is potentially hazardous if ingested. It can also damage acrylic/fibreglass pool and hot tub shells.
4. Polyhexamethylene biguanide (C8H17N5)n
- Polyhexamethylene biguanide (PHMB) is the generic name for the third chemical approved by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) as a disinfectant (sanitizer) used for microbiological control.
- Biguanides lack oxidation capability; therefore, to oxidize the organics, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is added because of its compatibility with biguanide.
- PHMB is not compatible with chlorine- or bromine-releasing chemicals, copper algaecides, and monopersulfate (MPS).
5. Potassium monopersulfate (KHSO5)
- Potassium monopersulfate is an oxygen-based oxidizer (not a sanitizer) used to remove organic buildup.
- Effectively removes organics that cause chloramine formation.
- Eliminates existing chloramines.
- Will not bleach vinyl liners.
- Dissolves quickly.
- Produces no odours like chlorine products.
- Swimmers can return to the water quickly after application.
Pool and hot tub water chemistry can be a complex subject. This article provides service technicians with an intermediate look at pool and hot tub water chemistry and testing. In a subsequent article, the author will discuss water balance and testing do’s and don’ts.
 Wayne J. Ivusich, BA, MS, CPO,® CPI,™ NSPF®I, is the manager of education for Taylor Technologies Inc., in Sparks, Md. He has been in the pool/hot tub industry for 27 years and has fielded technical questions from health officials, service technicians, distributors, dealers, and pool and hot tub owners about basic and advanced water chemistry. Ivusich, an experienced conference speaker and recognized industry expert, is a Certified Pool Operator (CPO®), a National Swimming Pool Foundation® Instructor (NSPF®I), and a member of the NSPF® Education Committee. He received his bachelor’s degree in 1987 and his master’s degree in 1995 from Towson University in Towson, Md. He can be reached via e-mail at wayne@taylortechnologies.com.
Wayne J. Ivusich, BA, MS, CPO,® CPI,™ NSPF®I, is the manager of education for Taylor Technologies Inc., in Sparks, Md. He has been in the pool/hot tub industry for 27 years and has fielded technical questions from health officials, service technicians, distributors, dealers, and pool and hot tub owners about basic and advanced water chemistry. Ivusich, an experienced conference speaker and recognized industry expert, is a Certified Pool Operator (CPO®), a National Swimming Pool Foundation® Instructor (NSPF®I), and a member of the NSPF® Education Committee. He received his bachelor’s degree in 1987 and his master’s degree in 1995 from Towson University in Towson, Md. He can be reached via e-mail at wayne@taylortechnologies.com.